Today, in the arsenal of modern dermatocosmetology tools, there is a fairly wide variety of methods for correcting skin aesthetic imperfections - chemical peels, mechanical dermabrasion, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, contour plastics and more. However, new directions and technologies in the beauty industry are constantly evolving and increasing.
This trend is very common for hardware methods, especially for laser treatment. The use of lasers, first in dermatology, and then in cosmetology, has had an impressive period. In fact since its emergence one of the newest laser treatment methods - selective photothermolysis - has passed more than 25 years. The pioneers of the field, Americans RR Anderson and JA Parrish, have determined the fate of fractional lasers in medicine, making them indispensable in such aesthetic treatments. skin imperfections such as capillary hemangioma. Port wine stains, hypertrichosis, tattoos, rosacea, pigmentation disorders, photoaging, wrinkles, etc.
Modern skin renovation techniques
We live in a time when more people are living to old age than ever before. And considering that many of them continue active lives, one of the most important issues in aesthetic medicine is the fight against skin aging.
Plastic surgery rejuvenates facial features by removing excess skin. However, at the same time, the skin still changes with time (age-related aging) or external factors (photoaging). It is also important that most patients look younger without surgery.
In that case, what method should be used to affect the skin and what should be done in it for a true rejuvenation?
All the methods that can be used to improve the appearance of the skin are joined by one principle - it exerts a traumatic effect on the skin, provokes fibrosis, which in turn leads to tension and compaction.
Currently, dermatocosmetology uses three main types of remodeling effects on the skin, including:
- chemical stimulation - chemical peeling with acids (trichloroacetic, glycolic, etc. );
- mechanical stimulation - mechanical dermabrasion, microdermabrasion, mesotherapy, fillers, needle subgrowing;
- thermal stimulation - laser ablation, heat removal using lasers and broadband light sources, radio frequency lifting, fractional method.
Chemical stimulation
Historically, acid exfoliation (peeling) was the first skin rejuvenation method. The principle of exfoliation is partial (like superficial exfoliation) or almost complete (such as middle and deep peeling) of the epidermis, damaging the fibroblasts and dermis structure. This damage activates an inflammatory reaction (the stronger it is, the greater the volume of damage itself), which causes additional collagen production in the skin.
However, to achieve the desired result, exfoliation has to sacrifice the epidermis. Experiments with burns have misled many people into allegedly "proving" that the epidermis is a self-regenerating organ that quickly recovers from damage. area. In this case, the peeling over time becomes more and more aggressive in relation to the epidermis (for example, deep phenolic peeling), until finally the accumulation of problems makes specialists aware of this cruelty. a method that ultimately leads to thinning of the skin.
Deep peelers ignore the issues that arise. Their essence is that due to the destruction of the papillae of the dermis and the weakening of nutrients, the epidermis becomes thinner, and the number of cells in the spiny layer is significantly reduced compared to what was before peeling. Decreased barrier function of the stratum corneum results in decreased skin hydration. (Therefore, almost all patients after deep peeling for a long time experience severe dryness of the skin. ) At the same time, the introduction of lighter skin practices (using trichloroacetic and fruit acids) did not meet their expectations for effective skin tightening.
Mechanical stimulation
From the method of mechanical stimulation of involutional changes in the skin, dermabrasion using a rotary device (v speed; cutter rotation up to 100, 000 rpm) deserves special attention. Currently, the modern Schumann-Schreus device is used (Germany)
This method can only be used in a surgical hospital, because this procedure requires anesthesia, postoperative wound surface care, a special toilet for the eyes and mouth, as well as a device for feeding the patient (due to the fact that postoperative edema that occurs 2-3 daysafter the procedure make it difficult to open the eyes and mouth).
This method is very effective, but unfortunately, with mechanical dermabrasion there is a high risk of complications such as:
- persistent postoperative hyperemia;
- the appearance of depigmented areas due to melanocyte damage when the cutter penetrates the basement membrane;
- wound surface infection;
- scar tissue (if the cutter is too deep in the skin)
All of the above has defined the limited applicability of this method in clinical practice.
Thermal stimulation
Ablative renovation
Since the late 1980s, lasers have been used to rejuvenate the skin by removing the tissue layer by layer (ablation) [4]. Careful and low-traumatic removal of the surface layer of the skin using a carbon dioxide laser stimulates the synthesis of its own collagen in it, the number of which increases several times after the procedure. Then gradually reset it.
The most effective is the use of a CO2 laser, when it is exposed to a deep thermal effect on all layers of the dermis, which is externally demonstrated by the skin tightening effect. This method was called "laser dermabrasion", or "laserresurfacing, " and in terms of efficiency it could not be challenged by other skin rejuvenation methods available at that time (Fig. 1).
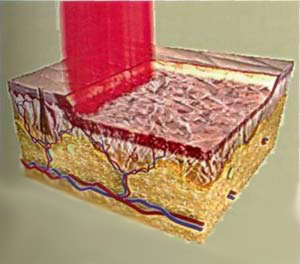
Image. 1. Traditional laser skin resurfacing scheme (laser dermabrasion)
However, CO2 lasers also cause many complications. Moreover, further research has shown that such a profound effect on the dermis stimulates fibrous tissue formation to a greater extent than contributes to new, normal synthesis. oriented collagen [5]. Fibrosis that develops can make the skin look unnaturally pale. Collagen that is synthesized after treatment is reabsorbed after several years, much like the collagen that builds up at the scar site. As a result of thinning of the epidermis caused by the atrophy of the papillary layer of the dermis, fine wrinkles begin to appear on the skin. Due to the weakening of the barrier function of the stratum corneum, the hydration level of the skin decreases, and it looks atrophy.
The Erbium-aluminum-yttrium garnet-erbium laser came later. The advantages of an erbium laser include a shallower depth of thermal penetration (an erbium laser penetrates to a depth of 30 microns, a CO2 laser - up to 150 microns) and (as a consequence) a lower risk of burns and tissue carbonization, as well as a relatively low cost (compared to a carbon dioxide laser)), attracting the attention of many specialists around the world.
However, as experience accumulates in working with these two types of installations, opinion has developed among specialists that CO2 lasers are more efficient [6]. Despite the negative effects of carbon dioxide laser dermabrasion described above, this method is still indispensable for the correction of acne scars. Additionally, it can be considered an alternative to surgical skin tightening - of all remodeling methods, only CO2 laser exposure can actually cause collagen contraction with a visible clinical lifting effect.
The problem with all of the methods described above is that they often "sacrifice", that is, significantly damage the epidermis. To rejuvenate your skin and truly look youthful, you need a perfect epidermis with natural papillary dermis, good hydration, normal skin tone and elasticity. The epidermis is a very complex highly specialized organ, up to 200 microns thick, which is our only defense against the influence of negative environmental factors. Therefore, whatever we do to rejuvenate the skin, we need to make sure that the normal underlying architecture is never broken.
This concept contributed to the emergence of non-ablative skin renovation technology.
Renovate non-ablative
The most common devices for non-ablative skin remodeling are neodymium (Nd-YAG) lasers and diodes, as well as broadband light sources (IPL). The principle of their action - selective photothermolysis - consists in heating and destroying the structure, containing sufficient amounts of melanin or oxyhemoglobin. In the skin, these are the accumulation of melanocytes (lentigo, melasma) and microvessels (telangiectasia), respectively. The emitted wavelengths used in non-ablative lasers correspond to the maximal absorption spectrum of oxyhemoglobin or melanin. Treatment procedures with non-ablative lasers and IPL are quite safe, have minimal rehabilitation period, however such treatments only remove pigment and cosmetic defects. In this case, there is a certain thickening of the skin, but the effect obtained is short-lived.
Fractional Skin Remodeling Techniques
The constant search for a new, highly effective and at the same time safe skin rejuvenation method has led to the emergence of a revolutionary technology - fractional laser radiation delivery. The proposed skin rejuvenation methods have been specially designed to overcome some of the above difficulties. Unlike "conventional" ablative and non-ablative laser methods, which are designed to achieve uniform thermal damage to the skin at a certain depth, the fractional method makes it possible to achieve selective microscopic thermal damage in the form of altered multiple columns leaving an unaffected area around the wound. this micro. Currently, the industry produces two types of fractional lasers: non-ablative and ablative.
The first uses an erbium doped optical fiber that produces radiation at a wavelength of 1550 nm. Laser fractures thousands of skins and tens of thousands of micro-defects in the form of columns - microthermal treatment zones (MLZ) - with diameters of 70-150 mk depth to 1359 mcm
As a result, about 15-35 skins are photocoagulated in the treated area. The chromophore for the laser is water. Coagulation occurs mainly in the lower layers of the epidermis and dermis. The stratum corneum remains intact because it contains a relatively small amount of water, and this significantly reduces the risk of infection. Epidermal recovery is rapid due to the low volume of lesions and the short distance of keratinocyte migration. The healing period is accompanied by moderate edema and hyperemia, followed by desquamation, appearing on days 5-7. Patient practically does not lose social activity.
This technology - fractional photothermolysis (FF) - is a highly effective method for non-ablative fractional skin rearrangement. To achieve the desired effect, course treatments are prescribed. Depending on the clinical situation, it is recommended to carry out from 3 to 6 procedures at intervals of 4-6 weeks. As with other non-ablative skin rejuvenation methods, the final result can be seen only 4-8 months after the procedure (cumulative effect).
In cases where a more aggressive effect on the skin is required - for scar correction, removing deep wrinkles and excess skin, the fractional ablation method (FA, or fractional deep dermal ablation -FDDA) is used.
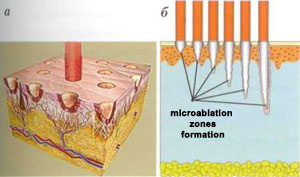
The fractional ablation method combines the advantages of a CO2 laser and the fractional principle of laser radiation delivery. In contrast to traditional CO2 lasers, which remove the entire surface layer of skin layer by layer, FA units form a large number of microablatives. zones (MAL) up to 300 µm in diameter at 350 to 1800 µm of evaporation depth (Fig. 2).
So, during this procedure, laser radiation, penetrates deep into the skin layers, destroying the top layer of the epidermis. In terms of efficiency, fractional ablative laser rejuvenation can be compared to plastic surgery, this is how deep the laser beam reappears.
Image. 2. The principle of operation of the fractional ablative laser: the formation of a microablative zone - MAZ (a); the dependence of the depth of the MAZ formation on the laser radiation power (b)
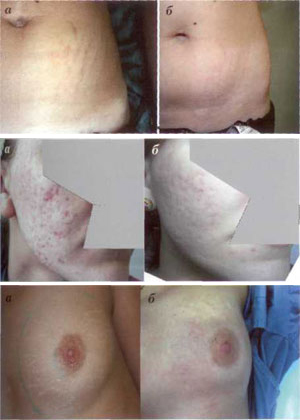
As with FF, from 15 to 35% of the skin in the treated area is completely exposed (in some cases, up to 70%). Recovery after the FA procedure is faster than after ablation layer by layer. This is due to the significant fact that parts of the epidermis and stratum corneum remain intact. Skin bleeding was observed for some time immediately after the procedure, but stopped immediately (Fig. 3 a, b).
Image. 3. Skin restoration measures after fractional ablation procedure: see immediately after treatment (a); every day (b); after 5 days (c); 14 days (d) after one
procedure
Many microbleds appear in the dermis, which causes a flow of complex changes leading to the production of new collagen. After the bleeding has stopped, it is necessary to drain the serous fluid that remains on the surface of the skin. Discharge was observed within 48 hours after the procedure, until complete epithelization of the microablative zone occurred. During this period, the patient uses special wound healing external agents. Usually starting from 3-4 days of peeling and swelling increases (Fig. 3 c). By the 7th day, this phenomenon gradually subsided, and erythema remained the only visible side effect (Fig. 3d). The duration of erythema depends on the laser exposure parameters and the vascular features of the skin. According to the author's observations, erythema lasts no more than 3 months.
The loss of social activity of the patient after the FA procedure lasts from 5 to 10 days.
To prevent scarring and the manifestation of post-inflammatory pigmentation, the skin needs to be treated with care. Decorative cosmetics can be used from 4-5 days. A prerequisite for good results is use for at least 3 months after a cosmetic sunscreen procedure with a high level of protection (SPF of at least 50). The risk of postinflammatory pigmentation occurs in 20% of patients and is generally higher in skinned patients with IV-V prototypes. Such hyperpigmentation is temporary and can last from 1 week to 3 months, which also depends on the depth of treatment and the area of the treated area. For prevention 1-2 weeks before the procedure and for 2 weeks thereafter, external agents based on hydroquinone (4%) and tretinoin (0. 1%) are prescribed. The main effects on facial skin after the FA procedure are as follows: noticeably tightens and reduces excess skin, evens out wrinkled skin, as well as acne scarred skin, reduces dyschromia, porosity.
This method has been tested by the author and his colleagues to remove stretch marks on the skin. As shown by clinical studies, this method has shown high efficiency in removing almost all types of stretch marks, both of which are acquired at puberty. period and postpartum. It is noted that the healing process on body skin is different from facial skin.
Skin reshuffle mechanism when using fractional laser
Let's consider the skin reshuffle mechanism when using a fractional laser.
After laser exposure, aseptic inflammation develops in the micro-wound area that has formed. The more aggressive the laser exposure, the more pronounced the inflammatory response, which actually stimulates post-traumatic release. growth factors and infiltration of tissue damaged by fibroblasts. The automatically approaching reaction is accompanied by a burst of cellular activity, which inevitably leads to the fact that the fibroblasts start producing more collagen and elastin. The skin makeover process includes three classic regeneration phases:
- phase I - changes (tissue inflammation). Start immediately after crash;
- phase II - proliferation (tissue formation). It starts 3-5 days after injury and lasts about 8 weeks;
- phase III - network renovation. Lasts from 8 weeks to 12 months.
It should be noted that all three phases of skin remodeling were observed both after fractional photothermolysis and after fractional ablation. But in the first case, the destructive effect of the laser is quite aggressive, as a result of which the inflammatory cascade of changes is never too wild.
A completely different image was observed after laser exposure to fractional ablation. The trauma caused by this laser damages the blood vessels, and the blood cells, along with the serum, are released into the surrounding tissue. Full mechanism of skin regeneration - pha change begins - aseptic inflammation develops. Platelets released from damaged vessels play an important role in activating blood clotting and releasing chemotoxic factors which, in turn, attract other platelets, leukocytes, and fibroblasts. Leukocytes, especially neutrophils, participate in the cleaning of damaged tissue, remove fragments of necrotic tissue, which are partially destroyed by phagocytitis, and partially exit to the skin surface in the form of microscopic debris consisting of epidermal and dermal tissue substrates and melanin - microepidermal necrotic debris (MENO).
The proliferation phase begins in about 5 days. During this period, neutrophils are replaced by monocytes. Monocytes, keratinocytes and fibroblasts continue to influence growth factors and at the same time are under the opposite influence. Keratinocytes stimulate epidermal growth and the release of growth factors needed to stimulate collagen production by fibroblasts. In this phase, new blood vessels are formed, and the extracellular matrix is formed intensively.
The final, reconstructive, healing phase after fractional laser exposure lasts several months.
On the 5th day after injury, the fibronectin matrix "fits" along the axis where the fibroblasts line up and where collagen will form. An important role in the formation of this matrix is played by transforming growth factor β (TGF-β is a chemotoxic agent for fibroblasts), as well as other growth factors. The main form of collagen in the initial phase of wound healing is collagen type III (this type of collagen is located in the upper layer of the dermis, just below the basal layer of the epidermis). The longer the alteration phase, the more collagen type III will be produced, however, the amount increases to a maximum from 5 to 7 days after breakdown. Collagen type III is gradually replaced by collagen over about a year Type I, which strengthens the strength of the skin. The blood circulation gradually normalizes, the skin becomes smoother and acquires a natural color.
Comparative analysis of laser methods for
skin remodelingSummarizing the above, here is a diagram showing the relationship between the effectiveness and safety of the laser skin remodeling technique.
The advantages of the fractional track rejuvenation method. The advantages of the fraction method used in clinical practice include:
- controls minimal skin damage. Histological studies carried out after the procedure showed an increase in the number of papillae in the dermis, which indicates the changes that occur in the skin as productive regeneration;
- effective rejuvenation: skin becomes thicker, collagen and elastin production increases significantly (more than 400% (! ));
- short healing time: mean 3 days after FF and 7-14 days after PA;
- minimal risk of hyperpigmentation;
- the possibility of performing the procedure on a patient with thin skin;
- the ability to have a healing effect on any part of the body;
- the possibility of using a mild type of anesthesia: with fractional photothermolysis, only local application anesthetics are used; for fractional ablation, a combination of conduction and infiltration anesthetics is required;
- loss of telangiectasis (due to the fact that there was a rupture of the blood vessels in many places making recovery impossible).
The main indications for fractional treatment
Indication for fractional photothermolysis:
- increases skin density in the early stages of aging. The FF procedure is relatively easy and can be done fearlessly. The therapeutic effect can be applied to the neck, décolleté, arms, stomach, thighs, mammary glands;
- skin photoaging;
- hyperpigmentation, melasma;
- hypertrophic scar;
- stretch marks.
Indication for Fractional Ablation:
- wrinkles of varying severity - from fine to very clear (in grooves);
- age-related loss of skin elasticity and firmness;
- excess skin on the eyelids, neck, face (as an alternative to plastic surgery);
- uneven skin texture;
- pronounced photoaging on the skin;
- acne scars;
- cicatricial deformity of skin after injury, surgery;
- hyperpigmentation: melasma, lentiginosis, speckled pigmentation, etc.
- vascular dystromia;
- stretch marks;
- actinic keratoses.
In conclusion, a few words about the prospects for using laser technology in aesthetic medicine. We have to pay tribute to manufacturers that they are starting to pay more attention to the safety of laser medical procedures. Technology is constantly developing. However, often the safety of a method is sacrificed to increase its effectiveness. Or vice versa. A compromise was found in the new principle of delivering laser radiation to tissues. It should be noted that the types of lasers remain the same: erbium, carbon dioxide, neodymium. This indicates that:
- First, laser skin remodeling is recognized as the most effective today;
- second, the breadth of coverage of aesthetic and dermatological problems resolved by this method is enormous - from skin rejuvenation to treatment of congenital and acquired skin pathologies;
- Third, with the advent of fractional technology, the safety and effectiveness of treatment has become predictable.














































































